WebSphere MQSeries Adapter
- Home
- Neuron ESB
- Development
- Developing Neuron Applications
- Connecting to External Systems
- Adapters
- Neuron Adapters
- WebSphere MQSeries Adapter
Overview
The Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter allows Neuron ESB to interact with IBM WebSphere MQSeries in a variety ways, from monitoring MQSeries Queues to placing data into MQSeries Queues, either through local or remote Queue Managers. The adapter allows Neuron ESB to manage and expose an IBM WebSphere MQSeries Queue as another messaging endpoint that any client on the bus can communicate with, without knowledge of IBM WebSphere MQSeries technology. The adapter supports a number of message exchange patterns (MEPS), exposing them as Modes of the adapter.
Once the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter is registered and an Adapter Endpoint is created, all configuration is managed through the property grid of the Adapter located on the properties tab of the Adapter Endpoint’s Details Pane as shown in Figure 1.
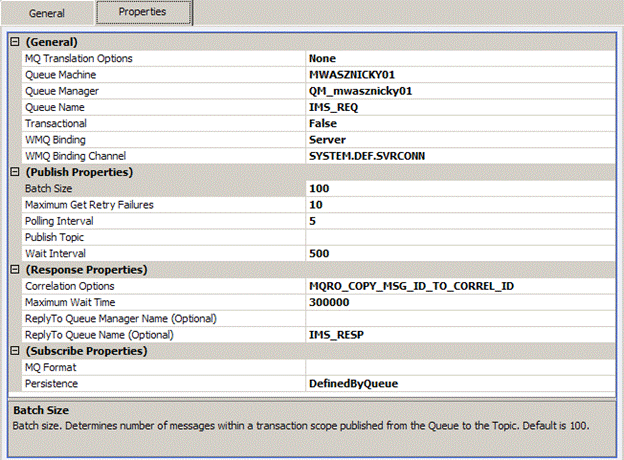
Features
The Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter supports a number of IBM MQSeries features, including the following:
- Client side API Support
- Server side API Support
- Extended Transactional Client
- Correlation Options
- XA Transactions
- EBCDIC translations
- Support for MQMD, MQRFH2, MQDLH, MQCNO, MQCIH (CICS) and MQIIH (IMS) headers
Requirements
The Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter is installed as part of the core Neuron ESB installation. The adapter is represented by 3 assemblies that are located within the \Adapters folder under the root of the default Neuron ESB installation directory:
- Neuron.Esb.Adapters.WebSphereMQ.dll
- Neuron.Esb.Adapters.WebSphereMQHeaderRW.dll
- Neuron.Esb.Adapters.WebSphereMQHeaders.dll
To use the adapter, it must be registered within the Neuron ESB Explorer Adapter Management Window. Within the Management Window, the adapter will appear with the name “WebSphere MQ Adapter”. Once registered, a new Adapter Endpoint can be created and configured.
The Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter supports connectivity to the following versions of IBM WebSphere MQSeries
- 6.0.2.6 and higher
If using the Client side API, the WebSphere MQSeries client must be installed on the Neuron server.
If using the Server side API, the WebSphere MQSeries server must be installed on the Neuron server.
If using Transactions with the Client side API option, then the IBM WebSphere Extended Transactional Client must be installed on the Neuron server.
Supported Modes
The Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter supports 4 modes of communication (MEPS) with IBM WebSphere MQSeries.
Publish
Publish mode allows Neuron ESB to monitor an IBM MQSeries Queue by regularly polling, de-queuing all the messages, and publishing those messages to a Neuron ESB Topic. Messages can be read either transactionally or non-transactionally and can be batched for performance. This is a one way MEP.
Configuration
Configuring the Publish mode of the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter requires that minimally, the following properties are set:
General Properties
- Queue Machine Name – Netbios name of MQSeries Server
- Queue Manager – Queue Manager for Request Queue
- Queue Name – Request Queue
- Transactional – True or False
- WMQ Binding – Determines client or server side API
- WMQ Binding Channel – Usually accept default.
Publish Properties
- Polling Interval – Number of seconds between Request Queue reads
- Publish Topic – Neuron ESB Topic to publish the MQSeries Request Message on. Corresponding Reply message will be received from this Topic and written to the ReplyTo Queue.
The defaults can be accepted for most other properties.
None of the properties within the “Subscribe Properties” or “Response Properties” section of the property page need to be set.
Subscribe
Subscribe mode allows Neuron ESB to write published messages to an IBM MQSeries Queue. Neuron ESB takes received ESB messages and will write them either transactionally or non-transactionally. This is a one way MEP.
Configuration
Configuring the Subscribe mode of the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter requires that minimally, the following properties are set:
General Properties
- Queue Machine Name – Netbios name of MQSeries Server
- Queue Manager – Queue Manager for Request Queue
- Queue Name – Request Queue
- Transactional – True or False
- WMQ Binding – Determines client or server side API
- WMQ Binding Channel – Usually accept default.
The defaults can be accepted for most other properties.
None of the properties within the “Publish Properties” or “Response Properties” section of the property page need to be set.
Request/Reply
Request/Reply mode allows applications (examples of which are z/OS CICS COBOL programs, AS/400 based programs, and other MQSeries host applications) to act as Neuron ESB service consumers with a synchronous request-response MEP using the IBM WebSphere MQSeries transport. Using this mode, an MQSeries based application could call any service provider application through Neuron ESB.
When acting as service consumer, the MQSeries application will put a message (MQ type REQUEST) on a request queue (MYREQ). The request message will specify (in MQ field ReplyToQ and ReplyToQMgr) where the application expects the response e.g. MYRESP queue and how (in MQ field Report) it wants to correlate the response. The MQ adapter will pick up the request message from the request queue (MYREQ) and publish it to the Neuron ESB bus as an ESB message with Request semantic. The adapter will wait for the response message on the bus, and when it arrives, it will put a message (MQ type REPLY) on the specified destination (ReplyToQ/ReplyToQMgr) e.g. MYRESP queue. The response message will be correlated as specified in the request. See Figure 2.
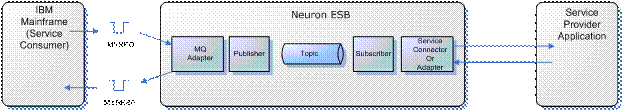
Configuration
Configuring the Request/Response mode of the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter requires that minimally, the following properties are set:
General Properties
- Queue Machine Name – Netbios name of MQSeries Server
- Queue Manager – Queue Manager for Request Queue
- Queue Name – Request Queue
- Transactional – True or False
- WMQ Binding – Determines client or server side API
- WMQ Binding Channel – Usually accept default.
Publish Properties
- Polling Interval – Number of seconds between Request Queue reads
- Publish Topic – Neuron ESB Topic to publish the MQSeries Request Message on. Corresponding Reply message will be received from this Topic and written to the ReplyTo Queue.
Response Properties
- Correlation Options
- ReplyTo Queue Manager Name
- ReplyTo Queue Name
The defaults can be accepted for most other properties.
Additionally, the ReplyTo Queue Manager and Queue Name can be overwritten at runtime by setting the following Neuron ESB custom adapter context properties:
- wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQ
- wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQMgr
Solicit/Response
Solicit/Response mode allows applications (examples of which are z/OS CICS COBOL programs, AS/400 based programs, and other MQSeries host applications) to act as Neuron ESB service providers with a synchronous request-response MEP using the IBM WebSphere MQSeries transport. Using this mode, an MQSeries based application could provide services to any client on the bus through Neuron ESB.
When acting as service provider, the MQSeries application will accept service requests on a queue (SREQ). It will process the request and put the response on a queue. The response queue might be fixed and defined by the application, but it can be specified in the MQ service request message, or specified as a property of the adapter.
In this mode, the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter will subscribe to request messages on the bus. When it receives a message it will put a message (MQ type REQUEST) on the request queue (SREQ). The adapter will specify (in MQ field ReplyToQ and ReplyToQMgr) where it expects the response e.g. SRESP queue and how (in MQ field Report) it wants to correlate the response. These values can be set as adapter properties and should be able to match the capabilities of the actual MQ application.
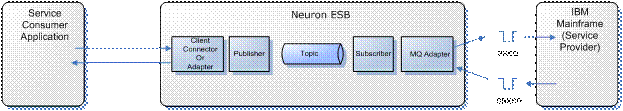
Configuration
Configuring the Solicit/Response mode of the Neuron WebSphere MQSeries adapter requires that minimally, the following properties are set:
General Properties
- Queue Machine Name – Netbios name of MQSeries Server
- Queue Manager – Queue Manager for Request Queue
- Queue Name – Request Queue
- Transactional – True or False
- WMQ Binding – Determines client or server side API
- WMQ Binding Channel – Usually accept default.
Response Properties
- Correlation Options
- ReplyTo Queue Manager Name
- ReplyTo Queue Name
The defaults can be accepted for most other properties.
Additionally, the ReplyTo Queue Manager and Queue Name can be overwritten at runtime by setting the following Neuron ESB custom adapter context properties:
- wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQ
- wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQMgr
None of the properties within the “Publish Properties” section of the property page need to be set.
Property Table
| Section Name | Property Name | Required | Description |
| General | These properties are used for all modes of the adapter | ||
| MQ Translation Options | Yes | Default is None. Options are None, UTF8 and Unicode. Used at runtime when reading messages from a queue using either Publish mode, Solicit/Response or Request/Response mode. If either UTF8 or Unicode are selected, message body translation will be attempted by using the ReadUTF or ReadString methods of the MQ Message. If None is selected, then the encoder will be determined by the MQ Message CharacterSet property. | |
| Queue Machine | Yes | Netbios name of the IBM WebSphere MQSeries Server | |
| Queue Manager | Yes | Name of the IBM WebSphere MQSeries Queue Manager | |
| Queue Name | Yes | Name of the IBM WebSphere MQSeries Queue | |
| Transactional | Yes | Default is False. True to use transactions. | |
| WMQ Binding | Yes | Default is Server. Options are Server or Client. This determines which API the adapter will use. If Server, then the IBM WebSphere MQSeries server MUST be installed on the Neuron ESB server. | |
| WMQ Binding Channel | Yes | Default is SYSTEM.DEF.SVRCONN. Options are SYSTEM.DEF.SVRCONN and SYSTEM.ADMIN.SVRCONN. Custom channel may be manually entered. | |
| Publish Properties | These properties are only used when the adapter is in either Request/Response or Publish mode. | ||
| Batch Size | Yes | Default is 100. Determines number of messages within a transaction scope published from the Queue to the Neuron ESB Topic. | |
| Maximum Get Retry Failures | Yes | Default is 10. Defines the maximum number of attempts to read the queue, when an error occurs during the read. Once the limit is reached, the Publish Adapter Endpoint will be disconnected. | |
| Polling Interval | Yes | Default is 5 seconds. The amount of time to wait to regularly poll the Queue for messages to publish to the Neuron ESB Topic. | |
| Publish Topic | Yes | Neuron ESB Topic to publish the MQ Message to. | |
| Wait Interval | Yes | Default is 500 milliseconds. Amount of time to wait for a message to arrive in the Queue being monitored (Polled). If no message is found, the queue is closed, and then checked during the next Polling Interval. If a message is found, the queue is immediately checked for another message, until no more messages are found. | |
| Response Properties | These properties are only used when the adapter is in either Solicit/Response or Request/Response mode. | ||
| Correlation Options | Yes | Default is MQRO_COPY_MSG_ID_TO_CORREL_ID. Options are MQRO_PASS_CORREL_ID, MQRO_USE_DEFAULT and MQRO_COPY_MSG_ID_TO_CORREL_ID. This property controls how the response message is correlated with the original request message and determines what value is written to the CorrelationID property of the Request message. | |
| Maximum Wait Time | Yes | Default is 5 minutes (300,000 milliseconds). Maximum amount of time to wait for a response message to be received. Minimum allowed value is 1000. Unlimited wait is not supported. If the Expiry property of the MQ Message is set (to not unlimited), that value * 10 will be used instead. | |
| ReplyTo Queue Manager Name | No | Optional. Only required if the ReplyTo Queue Manager Name is different from Request Queue Manager Name specified in the Queue Manager Name property of the General section. Corresponds to the IBM MQMD.ReplyToQMgr header property. | |
| ReplyTo Queue Name | No | Optional. Only required if the ReplyTo Queue Name is different from Request Queue Name specified in the Queue Name property of the General section. Corresponds to the IBM MQMD.ReplyToQ header property. | |
| Subscribe Properties | These properties are used with all modes of the adapter EXCEPT Publish. | ||
| MQ Format | Yes | Default is the MQ equivalent to NONE (padded empty string). Options are the MQ values of empty string (NONE) and MQSTR. This is used to set the MQ Message Format property. | |
| Persistence | Yes | Default is DefinedByQueue. Options are None, Persistent and DefinedByQueue . Used to set the persistence property of the Queue before the MQ Message is written to it. |
Many of the values within the Properties Table above can be configured and overridden by setting the appropriate IBM property or header value exposed through Neuron ESB custom properties. Please review the Metadata section below for more information.
Metadata
The Neuron ESB WebSphere MQSeries adapter exposes many of the IBM Properties and Header values as accessible Neuron ESB custom properties. The IBM Properties and Header values allow developers to provide a complete end-to-end solution that retains all message headers and properties from receipt to delivery; full fidelity of message-handling with no content or meta-data loss from end to end.
WebSphere MQ messages use a chained header of metadata that describes numerous types of information about the message including, but not limited to, metadata for JMS Queues, CICS Transactions, and Dead Letter queue data.
Each header contains the header data and data about the following header. The data about the following header includes the header name (for example, “RHF2 “), the CodedCharacterSetID, the Integer Encoding type (big endian or little endian), and the floating point encoding type.
When the Header name in the current header is blank “ “, then there is no header after the current one, and you have reached the last header before the message content.
Each header is defined in an IBM-provided C Header file named cmqc.h available with the WebSphere MQ SDK from IBM. The structure and field values are defined in the C Header file, which is used by the Adapter to decode and encode the headers on receipt and transmit.
These message properties affect the encoding and decoding of the actual message as it is transmitted.
Each header property is promoted to a Neuron ESB Custom property in the ESB message in the following format:
- PropertyName = wmq.Header. Property
- PropertyValue = String-encoded value of the property; that is, integers are converted to their string equivalents.
For example, the property name for the MQRFH2 StrucID would be “wmq.MQRFH2.StrucID” on an inbound message and the value would be “RHF2”.
Not all headers are currently supported. The supported headers include:
- MQMD
- MQRFH2
- MQDLH
- MQCNO
- MQCIH (CICS)
- MQIIH (IMS)
Refer to the IBM documentation for a list of all headers and properties associated with a WebSphere MQ Message.
NOTE: All message properties are assumed to have the default IBM values unless specifically overridden by the developer.
IBM WebSphere MQSeries Header properties
| Header Property Names |
| wmq.MQCIH.ADSDescriptor |
| wmq.MQCIH.AbendCode |
| wmq.MQCIH.AttentionId |
| wmq.MQCIH.Authenticator |
| wmq.MQCIH.CancelCode |
| wmq.MQCIH.CodedCharSetId |
| wmq.MQCIH.CompCode |
| wmq.MQCIH.ConversationalTask |
| wmq.MQCIH.CursorPosition |
| wmq.MQCIH.Encoding |
| wmq.MQCIH.ErrorOffset |
| wmq.MQCIH.Facility |
| wmq.MQCIH.FacilityKeepTime |
| wmq.MQCIH.FacilityLike |
| wmq.MQCIH.Flags |
| wmq.MQCIH.Format |
| wmq.MQCIH.Function |
| wmq.MQCIH.GetWaitInterval |
| wmq.MQCIH.InputItem |
| wmq.MQCIH.LinkType |
| wmq.MQCIH.NextTransactionId |
| wmq.MQCIH.OutputDataLength |
| wmq.MQCIH.Reason |
| wmq.MQCIH.RemoteSysId |
| wmq.MQCIH.RemoteTransId |
| wmq.MQCIH.ReplyToFormat |
| wmq.MQCIH.Reserved1 |
| wmq.MQCIH.Reserved2 |
| wmq.MQCIH.Reserved3 |
| wmq.MQCIH.Reserved4 |
| wmq.MQCIH.ReturnCode |
| wmq.MQCIH.StartCode |
| wmq.MQCIH.StrucId |
| wmq.MQCIH.StrucLength |
| wmq.MQCIH.TaskEndStatus |
| wmq.MQCIH.TransactionId |
| wmq.MQCIH.UOWControl |
| wmq.MQCIH.Version |
| wmq.MQCNO.ClientConnOffset |
| wmq.MQCNO.ClientConnPtr |
| wmq.MQCNO.ConnTag |
| wmq.MQCNO.Options |
| wmq.MQCNO.SSLConfigOffset |
| wmq.MQCNO.SSLConfigPtr |
| wmq.MQCNO.Version |
| wmq.MQCNO.strucId |
| wmq.MQDLH.CodedCharSetId |
| wmq.MQDLH.DestQMgrName |
| wmq.MQDLH.DestQName |
| wmq.MQDLH.Encoding |
| wmq.MQDLH.Format |
| wmq.MQDLH.PutApplName |
| wmq.MQDLH.PutApplType |
| wmq.MQDLH.PutDate |
| wmq.MQDLH.PutTime |
| wmq.MQDLH.Reason |
| wmq.MQDLH.StrucId |
| wmq.MQDLH.Version |
| wmq.MQIIH.Authenticator |
| wmq.MQIIH.CodedCharSetId |
| wmq.MQIIH.CommitMode |
| wmq.MQIIH.Encoding |
| wmq.MQIIH.Flags |
| wmq.MQIIH.Format |
| wmq.MQIIH.LTermOverride |
| wmq.MQIIH.MFSMapName |
| wmq.MQIIH.ReplyToFormat |
| wmq.MQIIH.Reserved |
| wmq.MQIIH.SecurityScope |
| wmq.MQIIH.StrucId |
| wmq.MQIIH.StrucLength |
| wmq.MQIIH.TranInstanceId |
| wmq.MQIIH.TranState |
| wmq.MQIIH.Version |
| wmq.MQRFH2.CodedCharSetId |
| wmq.MQRFH2.Encoding |
| wmq.MQRFH2.Flags |
| wmq.MQRFH2.Format |
| wmq.MQRFH2.NameValueCCSID |
| wmq.MQRFH2.NameValueData |
| wmq.MQRFH2.StrucId |
| wmq.MQRFH2.StrucLength |
| wmq.MQRFH2.Version |
| wmq.MQMD.StrucId |
| wmq.MQMD.Version |
| wmq.MQMD.Report |
| wmq.MQMD.MsgType |
| wmq.MQMD.Expiry |
| wmq.MQMD.Feedback |
| wmq.MQMD.Encoding |
| wmq.MQMD.CodedCharacterSetId |
| wmq.MQMD.Format |
| wmq.MQMD.Priority |
| wmq.MQMD.Persistence |
| wmq.MQMD.MsgId |
| wmq.MQMD.CorrelId |
| wmq.MQMD.BackoutCount |
| wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQ |
| wmq.MQMD.ReplyToQMgr |
| wmq.MQMD.UserId |
| wmq.MQMD.AccountingToken |
| wmq.MQMD.ApplIdentityData |
| wmq.MQMD.ApplOriginData |
| wmq.MQMD.GroupId |
| wmq.MQMD.MsgSequenceNumber |
| wmq.MQMD.Offset |
| wmq.MQMD.MsgFlags |
| wmq.MQMD.PutApplType |
| wmq.MQMD.PutApplName |
| wmq.MQMD.PutDate |
| wmq.MQMD.PutTime |
| wmq.MQMD.OriginalLength |
In addition to the Header properties, there are also Connection Properties that are accessible only programmatically. There are two components to an MQ connection—the Queue Manager connection and the Queue connection. Setting these Connection Properties at runtime can control how Neuron ESB manages the connections to these resources.
The Queue Manager connection includes some simple properties, such as the Queue Manager Name, and also includes properties like the MQOO_ property set.
The Queue connection includes the MQGMO_ and MQPMO_ (MQ Get Options and MQ Put Options).
The above properties are exposed by the following property-naming conventions:
- wmq.MQGMO.PropertyName
- wmq.MQOO.PropertyName
- wmq.MQPMO.PropertyName
IBM WebSphere MQSeries Connection properties
| Message Settings |
| Get Message Options (GMO) |
| wmq.MQGMO.ACCEPT_TRUNCATED_MSG |
| wmq.MQGMO.ALL_MSGS_AVAILABLE |
| wmq.MQGMO.ALL_SEGMENTS_AVAILABLE |
| wmq.MQGMO.BROWSE_FIRST |
| wmq.MQGMO.BROWSE_MSG_UNDER_CURSOR |
| wmq.MQGMO.BROWSE_NEXT |
| wmq.MQGMO.COMPLETE_MSG |
| wmq.MQGMO.CONVERT |
| wmq.MQGMO.FAIL_IF_QUIESCING |
| wmq.MQGMO.LOCK |
| wmq.MQGMO.LOGICAL_ORDER |
| wmq.MQGMO.MARK_SKIP_BACKOUT |
| wmq.MQGMO.MSG_UNDER_CURSOR |
| wmq.MQGMO.NO_SYNCPOINT |
| wmq.MQGMO.NO_WAIT |
| wmq.MQGMO.SET_SIGNAL |
| wmq.MQGMO.SYNCPOINT |
| wmq.MQGMO.SYNCPOINT_IF_PERSISTENT |
| wmq.MQGMO.UNLOCK |
| wmq.MQGMO.VERSION |
| wmq.MQGMO.WAIT |
| Get Match Type Options |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_CORREL_ID |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_GROUP_ID |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_MSG_ID |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_MSG_SEQ_NUMBER |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_MSG_TOKEN |
| wmq.MQMO.MATCH_OFFSET |
| Message Types |
| wmq.MQMT.APPL |
| wmq.MQMT.DATAGRAM |
| wmq.MQMT.REPLY |
| wmq.MQMT.REPORT |
| wmq.MQMT.REQUEST |
| Queue Option Options |
| wmq.MQOO.ALTERNATE_USER_AUTHORITY |
| wmq.MQOO.BIND_AS_Q_DEF |
| wmq.MQOO.BIND_NOT_FIXED |
| wmq.MQOO.BIND_ON_OPEN |
| wmq.MQOO.BROWSE |
| wmq.MQOO.FAIL_IF_QUIESCING |
| wmq.MQOO.INPUT_AS_Q_DEF |
| wmq.MQOO.INPUT_EXCLUSIVE |
| wmq.MQOO.INPUT_SHARED |
| wmq.MQOO.INQUIRE |
| wmq.MQOO.OUTPUT |
| wmq.MQOO.PASS_ALL_CONTEXT |
| wmq.MQOO.PASS_IDENTITY_CONTEXT |
| wmq.MQOO.SAVE_ALL_CONTEXT |
| wmq.MQOO.SET |
| wmq.MQOO.SET_ALL_CONTEXT |
| wmq.MQOO.SET_IDENTITY_CONTEXT |
| Message Put Option (PMO) |
| wmq.MQPMO.ALTERNATE_USER_AUTHORITY |
| wmq.MQPMO.CONTEXT |
| wmq.MQPMO.FAIL_IF_QUIESCING |
| wmq.MQPMO.LOGICAL_ORDER |
| wmq.MQPMO.NEW_CORREL_ID |
| wmq.MQPMO.NEW_MSG_ID |
| wmq.MQPMO.NO_SYNCPOINT |
| wmq.MQPMO.SYNCPOINT |
| Message Reporting Options (PMRF) |
| wmq.MQPMRF.ACCOUNTING_TOKEN |
| wmq.MQPMRF.CORREL_ID |
| wmq.MQPMRF.FEEDBACK |
| wmq.MQPMRF.GROUP_ID |
| wmq.MQPMRF.MSG_ID |
Messages
Defined messages are not required.